To find reconstitution info, click on 'COA' at the top of the page, enter the lot number and product size for the lot-specific COA.
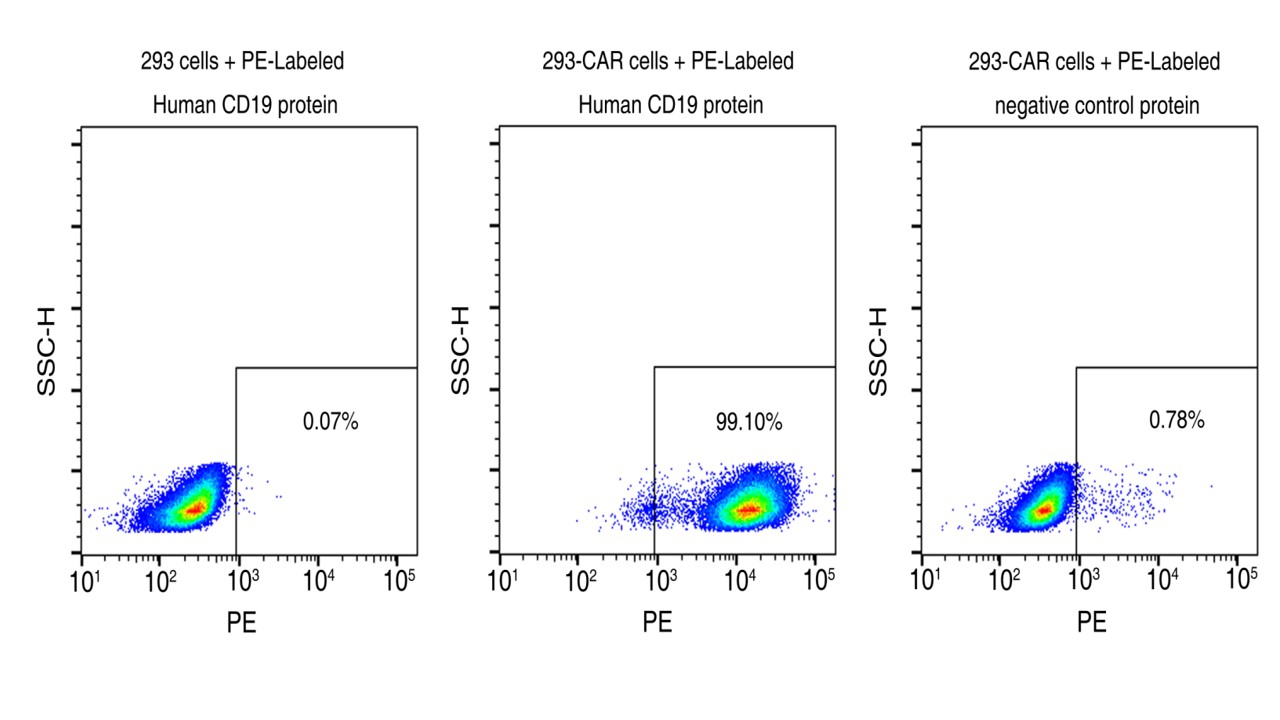
Flow cytometric analysis of anti-CD19 CAR expression. 5e5 of anti-CD19 CAR-293 cells were stained with 100 μL of 1:125 dilution of PE-conjugated human CD19 Protein (Site-Specific PE-Conjugated, ECD, His Tag, Cat. No. 11880-H08W1-SP) and negative control protein. Non-transduced 293 cells were used as a control (left). PE signal was used to evaluate the binding activity (QC tested). |
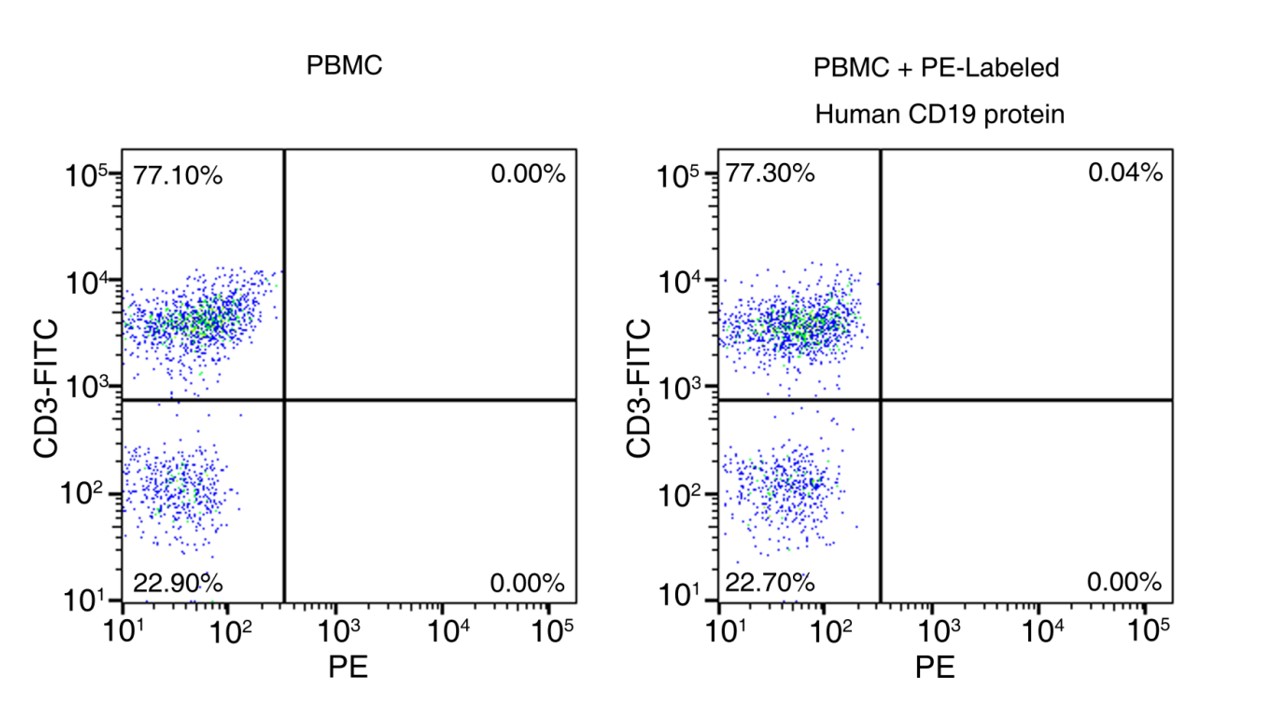
Binding activity of PE-conjugated CD19 protein to PBMC cells. PBMC cells were stained with FITC conjugated anti-CD3 antibody and PE-conjugated human CD19 Protein (Site-Specific PE-Conjugated, ECD, His Tag, Cat. No. 11880-H08W1-SP) and detected by flow cytometry. FITC signal was used to evaluate the content of CD3+ T cells in PBMCs. PE signal was used to evaluate the non-specific binding activity to PBMCs (QC tested). |
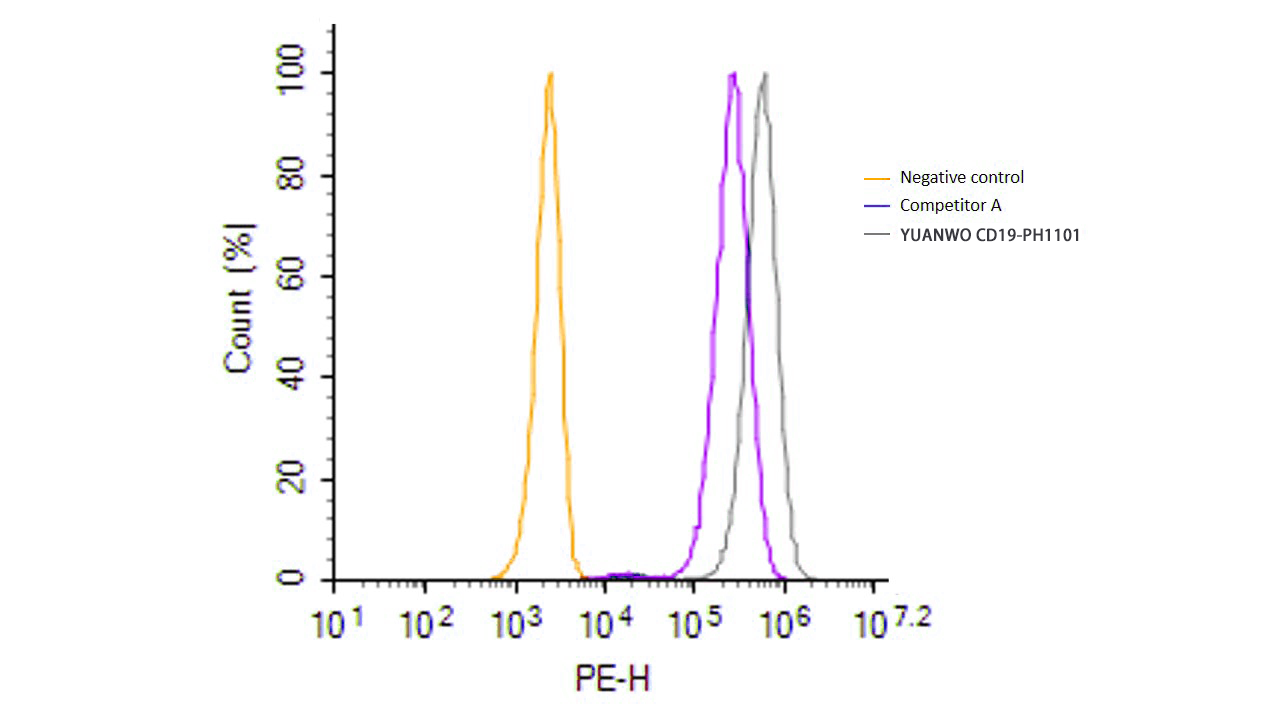 | 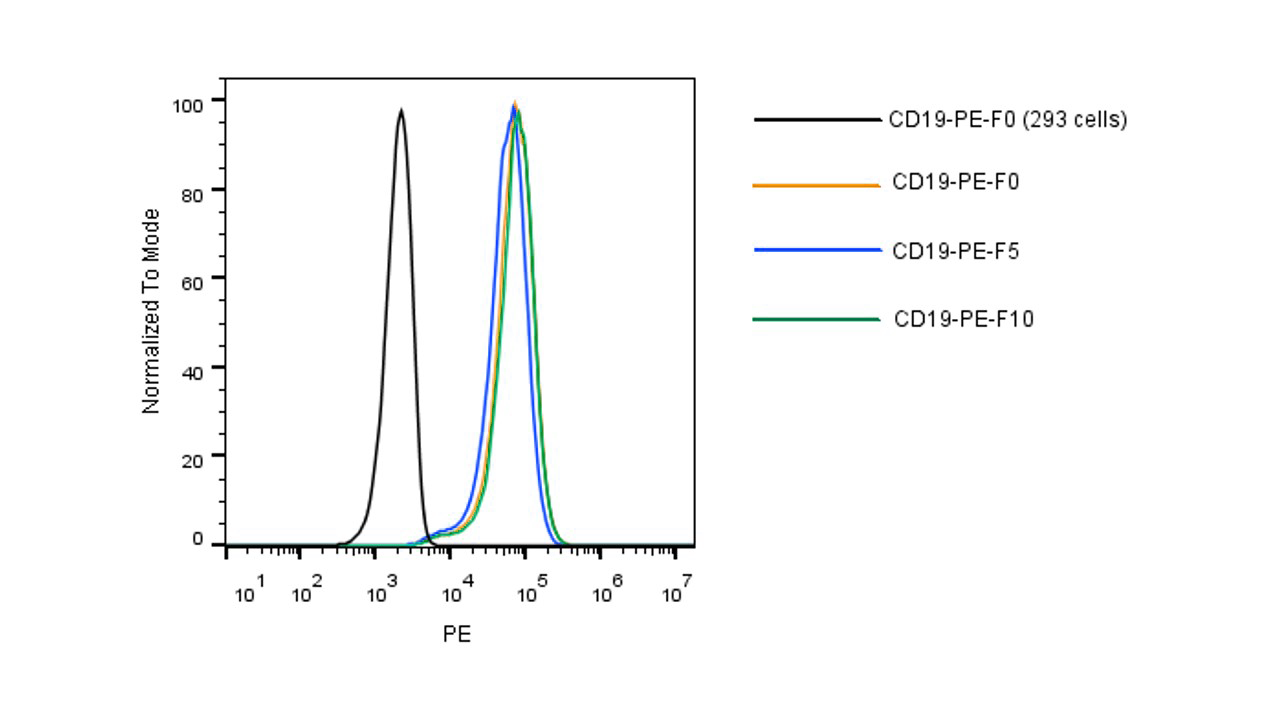 | |
| Flow cytometric analysis of anti-CD19 CAR expression. HEK293 cells were lentivirally transduced with anti-CD19 CAR. Non-transduced HEK293 cells were used as a control (shown on the left). 2 μL (1 test) of site-specifically PE-conjugated human CD19 protein from two vendors (competitor A and SINO) was used. The results demonstrated that SINO’s 11880-H08W1-SP has a much higher fluorescence intensity than that of the competitor (Routinely tested). | Flow cytometric analysis using PE conjugated CD19 protein. 5e5 of anti-CD19 CAR-293 cells were stained with PE-conjugated human CD19 protein (Site-Specific PE Conjugation, ECD, His Tag, Cat. No. 11880-H08W1-SP). Non-transduced 293 cells were used as a control (Black Histogram). The protein exhibited stable performance after multiple freeze-thaw cycles (5, 10 cycles). |
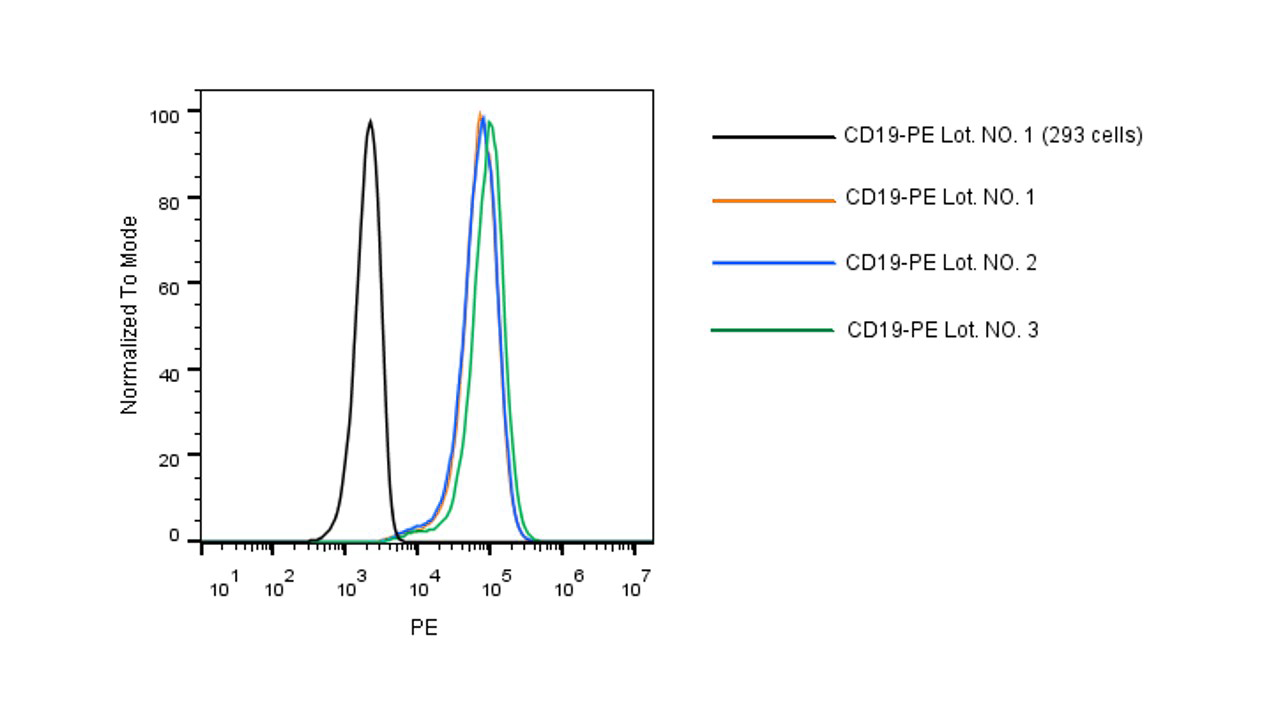
Flow cytometric analysis using different lots of PE conjugated CD19 protein. 5e5 of anti-CD19 CAR-293 cells were stained with 3 lots of PE-conjugated human CD19 protein (Site-Specific PE Conjugation, ECD, His Tag, Cat. No. 11880-H08W1-SP) at the same concentration. Non-transduced 293 cells were used as a control (Black Histogram). The results show high lot-to-lot consistency. |
B4 Protein, Human; CVID3 Protein, Human
The cluster of differentiation (CD) system is commonly used as cell
markers in Immunophenotyping. Different kinds of cells in the immune
system can be identified through the surface CD molecules associating
with the immune function of the cell. There are more than 320 CD unique
clusters and subclusters have been identified. Some of the CD molecules
serve as receptors or ligands important to the cell through initiating a
signal cascade which then alter the behavior of the cell. Some CD
proteins do not take part in cell signal process but have other
functions such as cell adhesion. Cluster of differentiation 19 (CD19) is
a member of CD system. CD19 is a cell surface molecule that assembles
with the antigen receptor of B-cells. This results in a descent in the
threshold for antigen receptor-dependent stimulation. A simplified view
holds that the ability of B-cells to respond to the various antigens in a
specific and sensitive manner is achieved in the presence of
low-affinity antigen receptors. CD19 primarily acts as a B-cell
co-receptor in conjunction with CD21 and CD81. The formation of the
receptor complex is induced by antigen and CD19, induced by exogenous
antigen, has been found cytoplasmic tail phosphorylated and bind to sIg.
Cancer Drug Targets
Zola H, et al. (2007) CD molecules 2006-human cell differentiation molecules. J Immunol Methods. 318 (1-2): 1-5.
Ho IC, et al. (2009) GATA3 and the T-cell lineage: essential functions before and after T-helper-2-cell differentiation. Nat Rev Immunol. 9 (2): 125-35.
Matesanz-Isabel J, et al. (2011) New B-cell CD molecules. Immunology Letters.134 (2): 104-12.
Carter RH, et al. (1992) CD19: lowering the threshold for antigen receptor stimulation of B lymphocytes. Science. 256 (5053): 105-7.