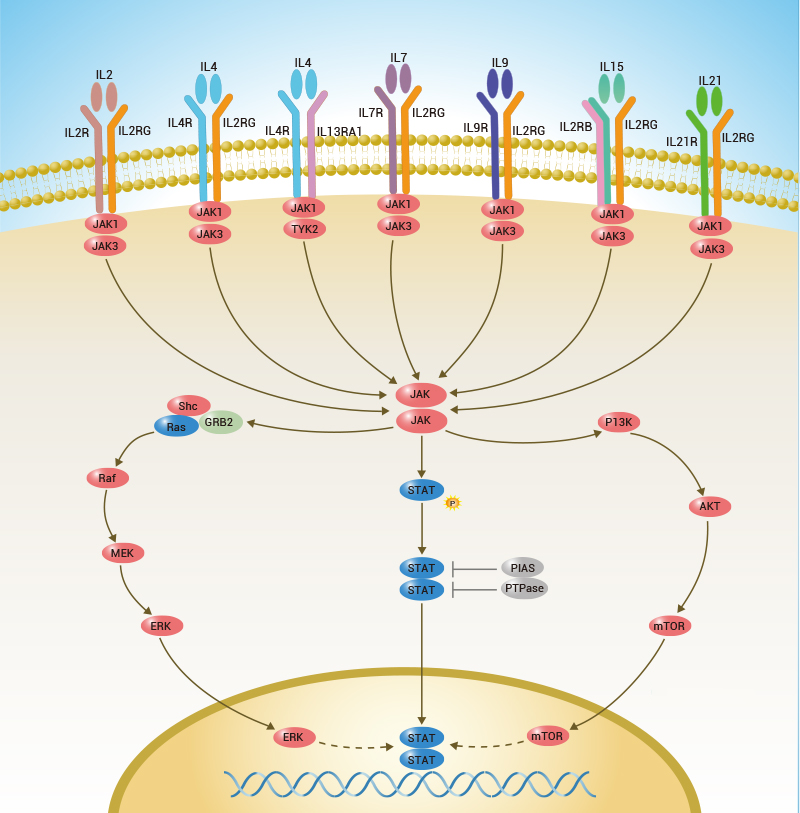
Interleukin 7 Receptor alpha (IL-7RA),
also known as CD127, is a 75 kDa hematopoietic receptor superfamily
member that plays an important role in lymphocyte differentiation,
proliferation, and survival. IL-7 receptor alpha (CD127) signaling is
essential for T-cell development and regulation of naive and memory
T-cell homeostasis. IL-7RA is critically required for the proper
development and function of lymphoid cells. Therefore, the IL-7RA is
critically required for the proper development and function of lymphoid
cells. Studies from both pathogenic and controlled HIV infection
indicate that the containment of immune activation and preservation of
CD127 expression are critical to the stability of CD4(+) T cells in
infection. A better understanding of the factors regulating CD127
expression in HIV disease, particularly on T(CM) cells, might unveil new
approaches exploiting the IL-7/IL-7R receptor pathway to restore T cell
homeostasis and promote immune reconstitution in HIV infection. Factors
relevant to HIV infection that could potentially decrease CD127
expression on human CD8(+) T cells. CD127 down-regulation may be an
important contributor to HIV-associated T-cell dysfunction. In addition
to IL-7, IL-7RA also associates with TSLPR to form the functional
receptor for thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) which indirectly
regulates T cell development by modulating dendritic cell activation.
Mutations in the human IL-7RA gene cause a type of severe combined
immunodeficiency in which the major deficiencies are in T cell
development, whereas B and NK cells are relatively normal in number.
Variation in the IL7RA gene was recently found associated with multiple
sclerosis (MS). The polymorphisms in the IL7RA gene is involved in MS
pathogenesis and suggest that IL7RA variation may primarily affect
chronic disease courses. Soluble CD127 (sCD127) appears to play an
important role in the immunopathogenesis of several chronic infections,
multiple sclerosis, and various cancers.
参考文献
Vranjkovic A, et al.
(2007) IL-7 decreases IL-7 receptor alpha (CD127) expression and
induces the shedding of CD127 by human CD8+ T cells. Int Immunol.
19(12): 1329-39.
Kiazyk SA, et al. (2008) Loss of CD127
expression links immune activation and CD4(+) T cell loss in HIV
infection. Trends Microbiol. 16(12): 567-73.
Akkad DA, et al. (2009) Variation in the IL7RA and IL2RA genes in German multiple sclerosis patients. J Autoimmun. 32(2): 110-5.
Crawley AM, et al. (2010) Soluble IL-7R alpha (sCD127) inhibits IL-7 activity and is increased in HIV infection. J Immunol. 184(9): 4679-87.