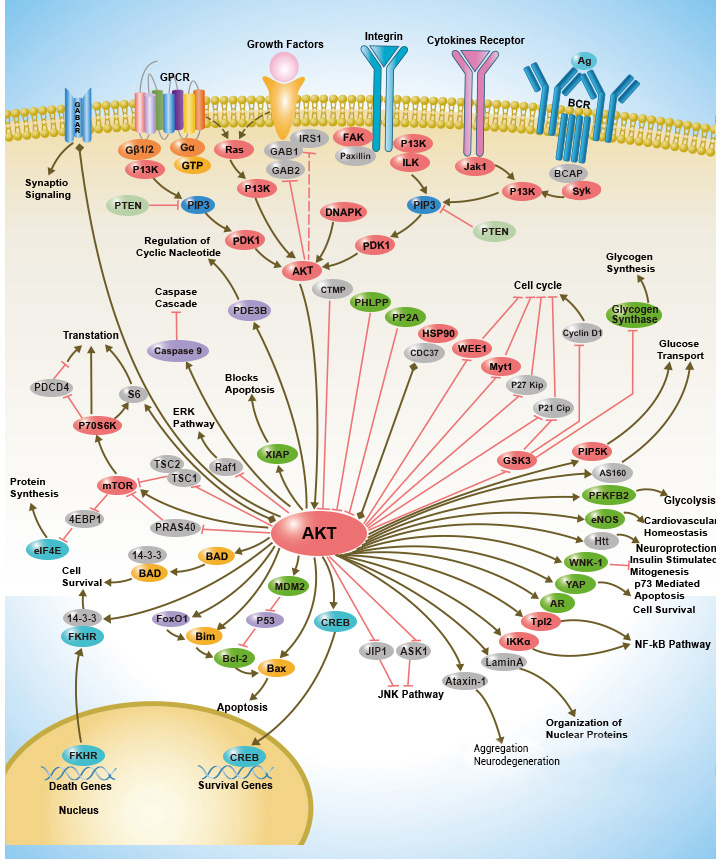
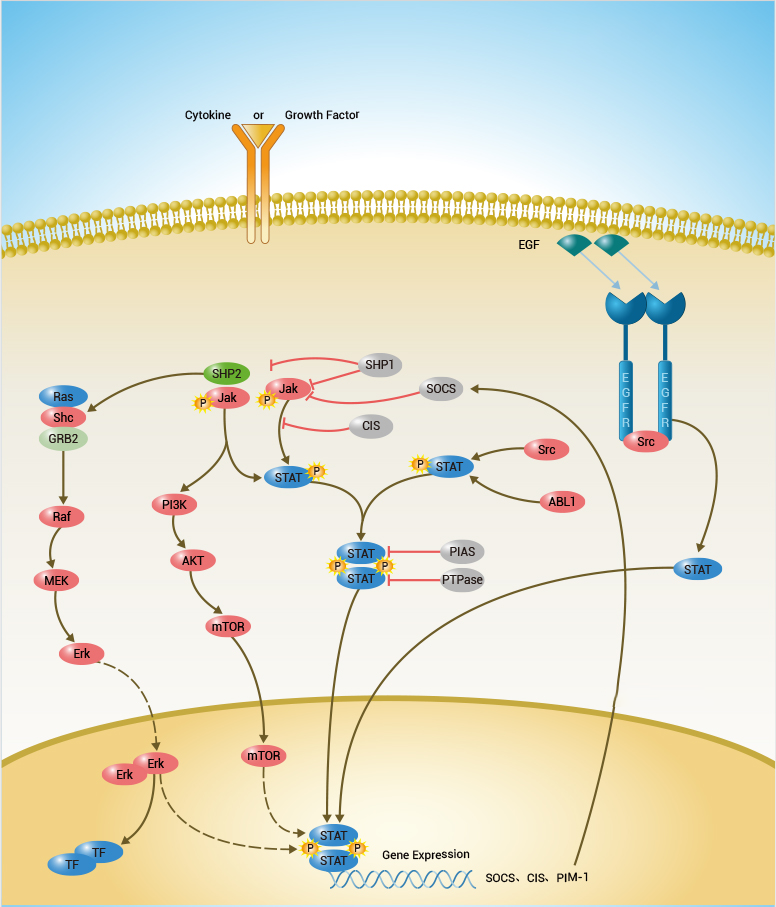
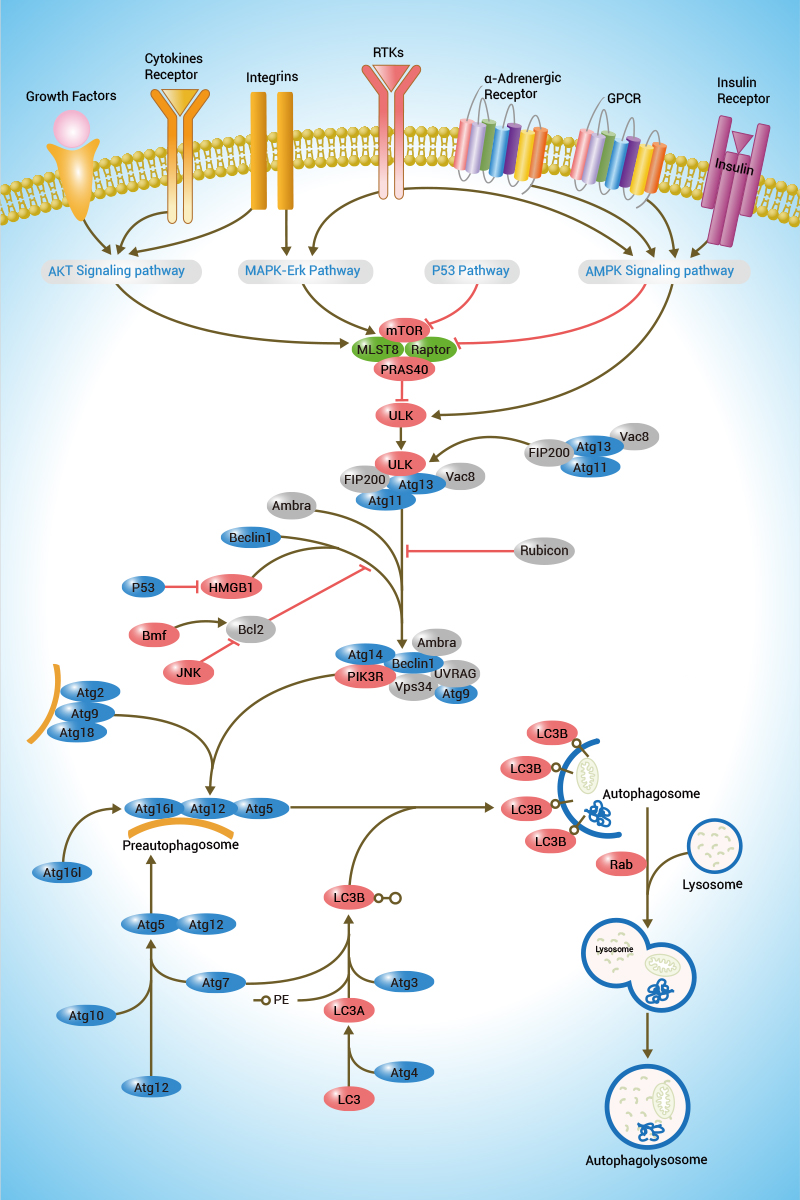
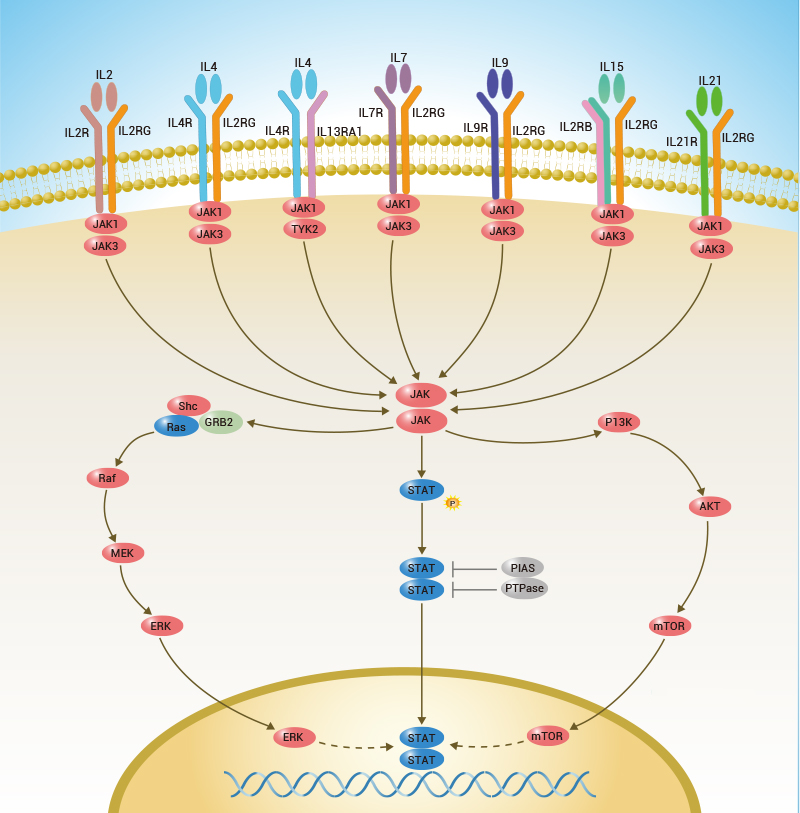
IL21 belongs to the IL-15/IL-21 family.
It is a cytokine with immunoregulatory activity. Cytokines are
proteinaceous signaling compounds that are major mediators of the immune
response. They control many different cellular functions including
proliferation, differentiation, and cell survival/apoptosis but are also
involved in several pathophysiological processes including viral
infections and autoimmune diseases. Cytokines are synthesized under
various stimuli by a variety of cells of both the innate (monocytes,
macrophages, dendritic cells) and adaptive (T- and B-cells) immune
systems. IL21 is expressed in activated CD4-positive T-cells but not in
CD8-positive T-cells, B-cells, or monocytes. It may promote the
transition between innate and adaptive immunity. IL-21 has been tried as
a therapy for alleviating allergic responses. It can significantly
decrease pro-inflammatory cytokines produced by T cells in addition to
decreasing IgE levels in a mouse model for rhinitis (nasal passage
inflammation).
参考文献
Coquet JM, et al. (2007)
IL-21 is produced by NKT cells and modulates NKT cell activation and
cytokine production. J Immunol. 178(5):2827-34.
Wei L, et al.
(2007) IL-21 is produced by Th17 cells and drives IL-17 production in a
STAT3-dependent manner. J Biol Chem. 282(48):34605-10.
Parrish-Novak
J, et al. (2002) Interleukin-21 and the IL-21 receptor: novel effectors
of NK and T cell responses. J Leukoc Biol. 72(5):856-63. 4 Kuchen S, et
al. (2007) Essential role of IL-21 in B cell activation, expansion, and
plasma cell generation during CD4+ T cell-B cell collaboration. J
Immunol. 179(9):5886-96.